Introduction
Meningitis is a serious infection of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Bacterial meningitis is the most serious type, and it can be fatal if not treated promptly.
One of the most common complications of meningitis is hearing loss. In fact, up to 30% of people who survive bacterial meningitis will experience some degree of hearing loss. The hearing loss can be mild, moderate, or severe, and it can affect one ear or both ears.
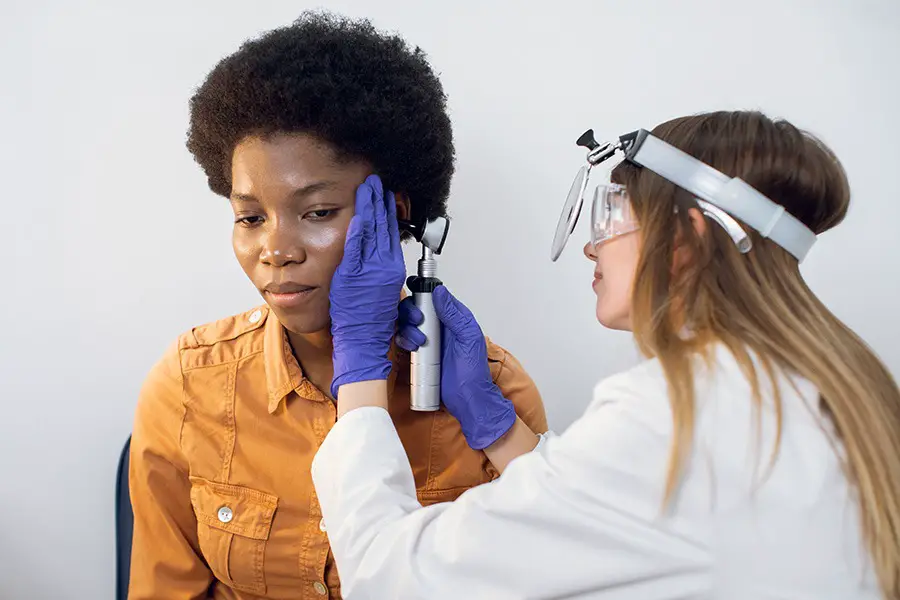
There are two main types of hearing loss that can be caused by meningitis: sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. Conductive hearing loss is caused by a blockage in the ear canal or middle ear.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss that can be caused by meningitis. It is caused by damage to the hair cells in the inner ear. The hair cells are responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. When the hair cells are damaged, they cannot send these signals to the brain, and this results in hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss is usually permanent. There is no cure for sensorineural hearing loss, but there are treatments that can help to improve hearing. These treatments include hearing aids and cochlear implants.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss is less common than sensorineural hearing loss. It is caused by a blockage in the ear canal or middle ear. The blockage can be caused by a number of things, including earwax, infection, or a tumor.
Conductive hearing loss is usually temporary. Once the blockage is removed, the hearing will usually return to normal. In some cases, conductive hearing loss may be permanent.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss is less common than sensorineural hearing loss. It is caused by a blockage in the ear canal or middle ear. The blockage can be caused by a number of things, including earwax, infection, or a tumor.
Conductive hearing loss is usually temporary. Once the blockage is removed, the hearing will usually return to normal. In some cases, conductive hearing loss may be permanent.
Treatment Options
There are a number of treatment options available for people who have hearing loss caused by meningitis. These options include:
- Hearing aids: Hearing aids are small, electronic devices that amplify sound. They can help people with hearing loss to hear better.
- Cochlear implants: Cochlear implants are surgically implanted devices that bypass the damaged hair cells in the inner ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve. They can provide a significant improvement in hearing for people with severe hearing loss.
- Speech therapy: Speech therapy can help people with hearing loss to improve their communication skills.
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent meningitis, but there are a number of things that can be done to reduce the risk. These include:
- Vaccines: There are vaccines available that can protect against some of the bacteria that cause meningitis.
- Good hygiene: Good hygiene practices, such as washing your hands frequently, can help to prevent the spread of infection.
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick: If you are around someone who is sick, avoid close contact with them. If you must be close to them, wear a mask.
Audien BTE (Behind the Ear) Rechargeable OTC Hearing Aid
Experience Unparalleled Sound Quality with the New Audien BTE (Behind the Ear) hearing amplifier. Elevate your hearing with the clearest, highest-quality sound available in an over-the-counter hearing assistance device. Designed by Audien, renowned for their sleek and comfortable hearing devices, the BTE model ensures exceptional hearing performance. It features advanced digital technology, including four environmental modes, background noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and two directional microphones per unit (four in total).
Say Goodbye to Missed Conversations and Hello to Superior Sound. Audien hearing devices excel at amplifying speech while reducing background noise, allowing you to effortlessly engage in conversations with friends and family. Experience the consistent, long-lasting, and sharp sound quality without any whistling or feedback issues. With customizable volume control, you can easily adjust the amplification to meet your individual needs. These devices are perfect for enhancing high tones and improving TV dialogue clarity.
Rechargeable for Uninterrupted Use. The Audien BTE hearing amplifiers are 100% rechargeable, offering convenience and freedom from the hassle of tiny button batteries. With wireless magnetic charging technology, you can enjoy a 20-hour battery life with just a quick two-hour charging time. The included charging case provides up to three full charges, giving you a total of 60 hours of amplified sound. Simply place the devices in the case, and they will wirelessly charge, ensuring you’re always ready to hear your best. Experience the ease and reliability of Audien sound amplifiers, ideal for individuals with dexterity issues or those tired of constantly purchasing and replacing batteries.
Mimi Hearing Test (iOS and Android)
Mimi Hearing Test stands out for its ability to integrate with Apple Health and its sleek, user-friendly interface. The app provides a comprehensive hearing test, resulting in a ‘hearing age’ that offers a simplistic way to understand one’s hearing capabilities. However, some users have reported that the test may be overly sensitive to background noise.
uHear (iOS and Android)
uHear provides three types of tests – a hearing sensitivity test, a speech in noise test, and a questionnaire about daily hearing situations. These three tests combined provide a rounded evaluation of one’s hearing. However, some users have noted that instructions could be clearer, especially for those who are not tech-savvy.
HearWHO (Android)
Developed by the World Health Organization, HearWHO allows users to check their hearing regularly and track changes over time. The app is praised for its simplicity and the credibility of its parent organization. However, it does not provide as many features as some of its competitors.
Phonak Leo – Interactive Stories (iOS)
Primarily designed for children, Phonak Leo uses interactive stories to test hearing abilities, making the hearing test a more engaging experience for young users. It’s colorful and fun, but it might not provide the level of detail required for adults seeking a comprehensive hearing analysis.
Decibel X (iOS and Android)
Decibel X is not a hearing test app per se. Instead, it’s a noise meter that helps users identify potentially harmful noise levels in their environment, making it a preventative tool. It’s highly accurate and professional-grade but does not offer personalized hearing tests.
A Comparison of the Apps
| App Name | Platforms | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mimi Hearing Test | iOS, Android | Hearing age score, Apple Health integration | Sleek interface, Comprehensive test | Sensitive to background noise |
| uHear | iOS, Android | Hearing sensitivity test, Speech in noise test, Daily hearing situation questionnaire | Rounded hearing evaluation | Instructions could be clearer |
| HearWHO | Android | Regular hearing check, Hearing tracking | Simple to use, Credible source (WHO) | Limited features |
| Phonak Leo – Interactive Stories | iOS | Interactive story-based hearing tests | Engaging for children | Not detailed enough for adults |
| Decibel X | iOS, Android | Environmental noise level meter | Accurate, Professional-grade | Not a personalized hearing test |
Mimi Hearing Test: Offers a ‘hearing age’ score that provides a simplistic understanding of hearing capabilities. Its sleek, user-friendly interface is highly appreciated by users. However, it may be overly sensitive to background noise.
uHear: Provides three types of tests – a hearing sensitivity test, a speech in noise test, and a questionnaire on daily hearing situations. These combined provide a comprehensive evaluation of one’s hearing. However, the instructions could be clearer, especially for individuals not familiar with technology.
HearWHO: Developed by the World Health Organization, HearWHO allows users to check their hearing regularly and track changes over time. While simple to use, it does not provide as many features as some competitors.
Phonak Leo – Interactive Stories: Primarily designed for children, Phonak Leo uses interactive stories to test hearing abilities. It makes the hearing test a more engaging experience for young users, but may not provide the level of detail required for adults seeking a comprehensive hearing analysis.
Decibel X: Although not a hearing test app, Decibel X is a noise meter that helps users identify potentially harmful noise levels in their environment. It’s a preventative tool and professional-grade but does not offer personalized hearing tests.
Each of these apps has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best one for you will depend on your specific needs and expectations.
Conclusion
Meningitis is a serious infection that can have a number of long-term effects, including hearing loss. If you have survived meningitis, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of hearing loss and to get prompt treatment if you experience any problems.
Here are some tips for managing hearing loss after meningitis:
- Get regular hearing tests. Your doctor or audiologist can monitor your hearing and make sure that you are getting the right treatment.
- Use hearing aids or cochlear implants. These devices can help you to hear better and communicate more effectively.
- Join a support group. Talking to other people who have experienced hearing loss can be helpful and provide you with valuable support.
- Get involved in advocacy work. You can help to raise awareness of hearing loss and advocate for better treatment options.
Hearing loss can be a challenging condition, but it is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many resources available to help you manage your hearing loss and live a full and active life.
Here are some additional resources that may be helpful:
- The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): The NIDCD is a federal agency that provides information and resources on hearing loss.
- The Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA): The HLAA is a nonprofit organization that provides support and advocacy for people with hearing loss.
- The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS): The AAO-HNS is a professional organization for otolaryngologists (ear, nose, and throat doctors).

Decoding Silence: An Analytical View on the Advances in Conductive Hearing Loss Research and Treatment
This analytical article sheds light on conductive hearing loss, offering an in-depth exploration of its genetic factors, treatment advances, and promising experimental therapies.
Embracing the Melody of Life: Navigating the Journey with Conductive Hearing Loss
A blog post delving into the experiences and challenges of living with conductive hearing loss, discussing its impact on everyday life, social interactions, mental health, and the potential benefits of hearing aids and cochlear implants.





