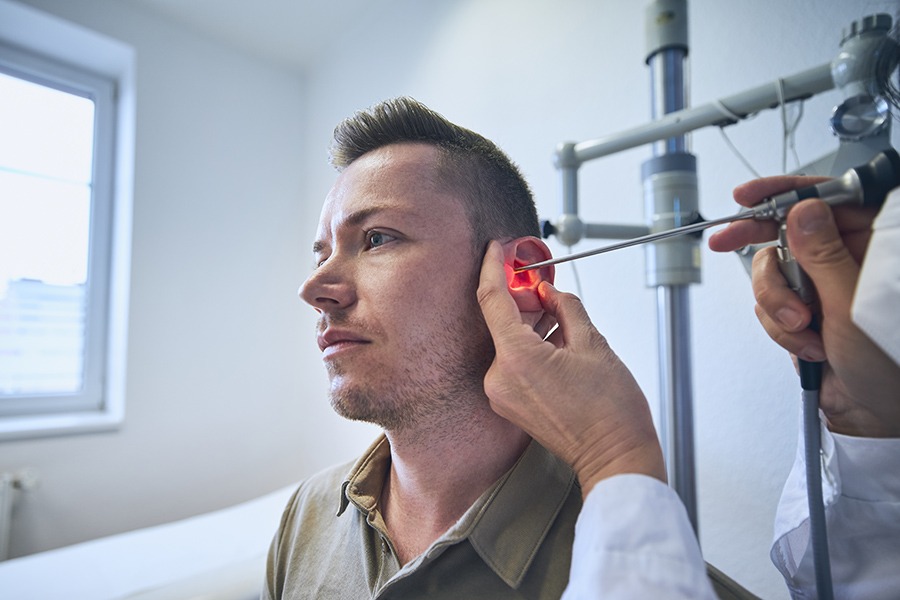
Introduction
Life is filled with countless sounds that we often take for granted—the melody of birds chirping in the morning, the soothing rhythm of rain falling on the rooftop, the soft whispers of loved ones. These auditory experiences create the symphony of life, imbuing our days with rich and immersive experiences. However, for those living with conductive hearing loss, this symphony is often muted or distorted, impacting their quality of life in significant ways.
Conductive hearing loss is a type of hearing impairment where the transmission of sound from the outer ear to the inner ear is blocked or reduced. This obstruction causes sound levels to be decreased, leading to difficulties in hearing. It’s a complex, multifaceted condition that can arise from various causes and manifest in numerous ways.
In this comprehensive guide, we aim to shed light on conductive hearing loss, making sense of its types, prevalence, genetic implications, differences from sensorineural hearing loss, and possibilities for reversal. With an empathetic tone and explanatory style, our intention is to empower you with knowledge and understanding of your condition, or of those dear to you living with this form of hearing loss.
The journey towards better hearing health and improved quality of life begins with knowledge and understanding. So, let’s embark on this journey together, exploring the intricate world of conductive hearing loss.
Prof-ReChargeable-Hearing-Aid
Experience Exceptional Sound Quality with Vivtone RIC02, a professional RIC hearing aid featuring a receiver in the canal design. Enjoy superior sound fidelity, reduced distortion, and minimal feedback. With a remarkable 51dB peak sound gain, it surpasses many other devices, catering to a wide range of hearing loss levels.
State-of-the-Art Technology awaits you with Vivtone RIC02. Designed with US-made components from renowned brands like Intricon and Knowles, this advanced device offers exceptional quality at a fraction of the cost. The built-in 30mAh steel-sealed lithium polymer battery charges rapidly in just 1.5 hours and provides an impressive battery life of over 20 hours.
Reliability and Water Resistance come hand in hand with the Vivtone RIC02. Secure your device with the included lanyard and clip, preventing accidental loss. With an IP65 rating, these hearing aids are resistant to water, sweat, and raindrops, assuring longevity and durability. Give the perfect gift to your seniors and loved ones, as this device combines functionality with an appealing appearance and packaging.
Types of Conductive Hearing Loss: A Comprehensive Overview
Conductive hearing loss is typically categorized based on the location of the problem in the ear – whether it’s in the outer ear, the ear canal, or the middle ear.
In cases where the outer ear or ear canal is affected, conditions like earwax build-up, swimmer’s ear (infection of the ear canal), or exostosis (abnormal bone growth in the ear canal) can lead to conductive hearing loss.
If the middle ear is the site of the problem, conditions such as otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear), otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth in the middle ear), or a perforated eardrum can be the culprits.
Interestingly, conductive hearing loss can also be a temporary condition. For instance, instances of ear infection (otitis media) or impacted earwax can lead to temporary hearing loss, which can be reversed once the condition is treated.
Prevalence and Epidemiology of Conductive Hearing Loss
The prevalence of conductive hearing loss varies across different regions and populations. According to the World Health Organization, it is estimated that over 5% of the world’s population – or 466 million people – have disabling hearing loss, with conductive hearing loss being a significant contributor.
Importantly, these figures tend to increase with age, with the highest prevalence observed in adults over 60 years of age. Geographical location, socio-economic conditions, and access to health care also significantly impact the prevalence of conductive hearing loss.
Interestingly, certain populations have a higher predisposition to specific causes of conductive hearing loss. For instance, indigenous populations living in cold climates have been found to have a higher incidence of otitis media and consequent conductive hearing loss.
Tinnitus: The Truth Behind That Annoying Ringing in Your Ears
The Role of Genetics in Conductive Hearing Loss
Genetics plays a significant role in many types of hearing loss, including conductive hearing loss. Certain genetic conditions, such as Treacher Collins syndrome, Pierre Robin syndrome, and Down syndrome, are known to cause anomalies in the structure of the ear, leading to conductive hearing loss.
Moreover, a condition known as otosclerosis, which causes abnormal bone growth in the middle ear and often leads to conductive hearing loss, has been shown to have a strong genetic component. Researchers have identified certain genes that are associated with an increased risk of developing this condition. Therefore, a family history of otosclerosis or other hereditary ear disorders can significantly increase one’s risk of developing conductive hearing loss.
In recent years, advancements in genetic testing have allowed for early detection and diagnosis of these conditions, enabling early interventions and potentially reducing the impact of hearing loss. However, the world of genetics is intricate and continually evolving, and further research is required to fully understand the complexity of genetic factors in conductive hearing loss.
Conductive vs. Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to hearing loss, understanding the difference between conductive and sensorineural forms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
As we discussed earlier, conductive hearing loss is due to problems with the ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear that prevent sound from being conducted effectively to the inner ear. In contrast, sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the nerve pathways that connect the inner ear to the brain.
In terms of symptoms, both types of hearing loss can result in reduced hearing ability. However, individuals with conductive hearing loss may often find that sounds seem quieter or muffled, while those with sensorineural hearing loss may struggle with understanding speech, even when the volume is adequate.
Moreover, the treatment approach varies significantly between these two types of hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss can often be treated with medications or surgery, while sensorineural hearing loss typically requires hearing aids or cochlear implants as the damage is usually irreversible.
Tinnitus: why it’s still such a mystery to science
Can Conductive Hearing Loss Be Reversed?
The answer to this question largely depends on the cause of the conductive hearing loss. When caused by conditions such as ear infections or impacted earwax, the hearing loss can often be reversed through treatment, which may include antibiotics for infections or earwax removal procedures.
However, in cases where conductive hearing loss is caused by structural issues within the ear, such as a malformation of the ear structures or otosclerosis, the treatment becomes more complicated. It may involve surgery to correct the anatomical problem or hearing aids to help amplify sounds.
It’s important to remember that every individual’s situation is unique. Therefore, what works for one person may not work for another. The key to managing and potentially reversing conductive hearing loss lies in accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Concluding this journey through the world of conductive hearing loss, we have explored its various types, examined its prevalence and epidemiological factors, understood the role of genetics, differentiated it from sensorineural hearing loss, and evaluated the possibilities for its reversal. Armed with this knowledge, individuals dealing with conductive hearing loss, or their loved ones, can better navigate their journey towards improved hearing health.
While the journey may seem challenging, remember that every step taken is a step towards better understanding, better management, and a better quality of life. Remember that you’re not alone on this journey. There’s a community of people who understand what you’re going through, healthcare professionals dedicated to helping you improve your hearing health, and countless resources (like this one) that are here to provide you with the information and support you need.
Together, we can navigate the echoes of conductive hearing loss, transforming them into a symphony of understanding, empathy, and better hearing health.
Conclusion
We sincerely hope that this guide has provided you with some clarity and understanding of conductive hearing loss. The world of hearing health can be complex, but with the right information and support, we believe that every individual has the potential to navigate their own unique journey towards better hearing health.
It’s important to remember that while information is a powerful tool, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of hearing loss, we urge you to consult with a healthcare provider or a hearing health professional. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and guide you towards the most effective treatment options.
Finally, remember that hearing loss, including conductive hearing loss, is a widespread condition, and there’s no need to feel alone or isolated. Countless individuals are experiencing similar challenges, and numerous support groups and resources are available to help you along the way.
Navigating the world of hearing health might seem daunting, but with each step, with each piece of knowledge gained, you are progressing towards a more empowered, informed, and healthier version of yourself. So keep going, keep learning, and keep advocating for your hearing health.
As we bring this guide to a close, let’s remind ourselves once again: The symphony of life is within reach, and together, we can navigate the echoes of conductive hearing loss.

Walking in Their Shoes: A Closer Look at the Lives of Seniors with Otosclerosis
Introduction Otosclerosis, a hearing condition that primarily affects the bones in the

Unveiling Otosclerosis: Understanding Its Impact and Navigating Life
Introduction Imagine the orchestra of life gradually tuning down until the world
REFERENCES
Hearing Link
A UK-based hearing loss organization offering information and support to individuals and families, including resources on conductive hearing loss.