Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in the Golden Years
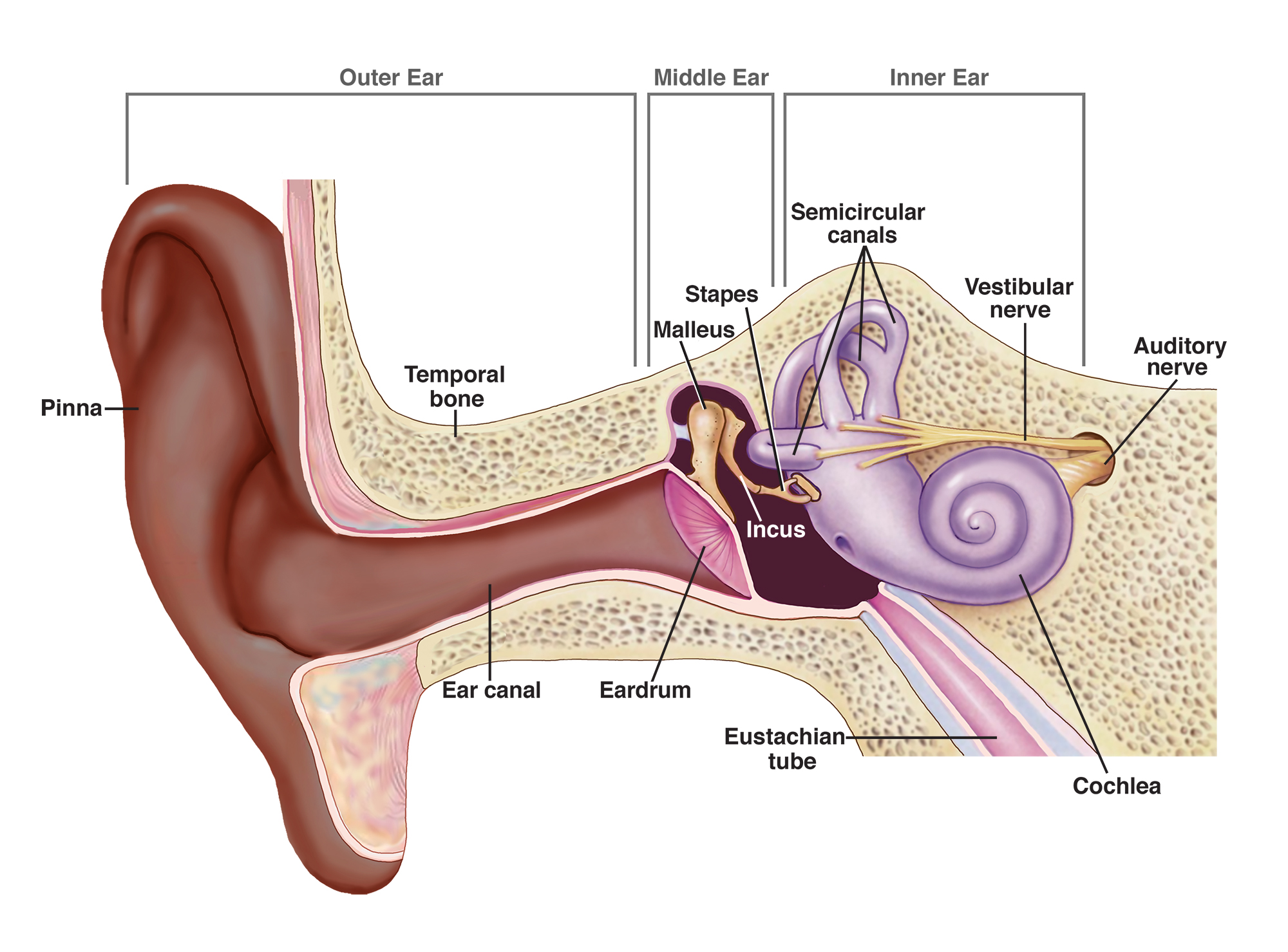
Otosclerosis, typically affecting the middle ear and leading to hearing loss, is a condition often associated with adults but also significantly impacts the elderly. This guide delves into the nuances of Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in older adults, offering caregivers essential insights for providing effective support.
Special Considerations for Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in the Elderly
As Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis progress with age, they present unique challenges. The elderly face multiple health issues, and the addition of these conditions to their health profile requires special considerations. Age-related changes in physical health, mental well-being, and lifestyle often influence the management of Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis. For instance, cognitive decline associated with aging can exacerbate the challenges posed by these conditions, making it difficult for the elderly to use hearing aids or remember healthcare instructions. Treatment plans must therefore consider these aspects to ensure adherence and effectiveness.
The Intersection of Otosclerosis, Otospongiosis, and Age-Related Hearing Loss
Understanding the intersection of Otosclerosis, Otospongiosis, and age-related hearing loss, also known as presbycusis, is crucial for caregivers. Presbycusis, characterized by gradual sensorineural hearing loss, differs from Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis, which typically result in conductive hearing loss. When an individual experiences both conditions, the combined effect can significantly impair hearing. Caregivers and healthcare providers must devise comprehensive strategies for diagnosis and treatment, considering both types of hearing loss.
Understanding the Unique Needs of Older Adults with Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
Recognizing the unique needs of older adults with Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis is vital. Beyond the medical aspects, their emotional well-being and quality of life are equally important. Dealing with hearing loss can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and depression among older adults. Caregivers can offer emotional support, encourage social interactions, and assist in communication, using alternative methods like visual cues or writing to ease daily interactions.
How Aging Affects the Progression and Management of Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
Aging significantly impacts the progression and management of Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis. Changes in the ear bones can accelerate the progression of these conditions, leading to more significant hearing loss. Additionally, age-related health conditions, such as arthritis or Parkinson’s, can complicate the management of these conditions, making it difficult for older adults to adjust hearing aids or attend regular medical appointments. Caregivers must understand these factors to provide effective support.
Supporting Seniors Living with Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis – A Caregiver’s Guide
Supporting a senior living with Otosclerosis or Otospongiosis requires patience, empathy, and practical skills. Helping older adults use hearing aids effectively, facilitating communication, and providing emotional support are key aspects of this role. Caregivers should also take care of their own well-being, as caregiving can be emotionally and physically demanding.
FAQs About Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in Elders
- What are Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis? Otosclerosis is a condition causing progressive hearing loss, while Otospongiosis refers to its early stages, particularly affecting older adults.
- How do these conditions impact elders? They affect not only hearing but also social interactions, daily activities, and mental health.
- What are the key strategies for managing these conditions in elders? Key strategies include understanding hearing aids, facilitating communication, and promoting social participation.
- Can these conditions lead to complete hearing loss in elders? If untreated, they can lead to significant hearing loss, but early intervention can mitigate this.
- Are there specific interventions for older patients? Yes, age-specific interventions like simpler hearing aids and assistive listening devices are beneficial.
- How can caregivers support elders with these conditions? Caregivers can support by promoting independence, understanding the condition, and advocating for the elder’s needs.
Practical Tips for Managing Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in Elders
- Learn About Hearing Aids: Understand how to operate and troubleshoot hearing aids.
- Facilitate Effective Communication: Use visual cues and clear speech to aid communication.
- Encourage Social Interaction: Help elders engage in social activities to prevent isolation.
- Adapt Home Environment: Modify the home to accommodate hearing challenges.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Ensure consistent audiologist visits and hearing aid maintenance.
Conclusion
Caring for older adults with Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis involves understanding the multifaceted impact of the conditions. By employing empathetic care strategies, personalizing interventions, and promoting independence, caregivers can significantly enhance the quality of life for elders with these conditions. This guide provides a foundation for caregivers to build upon, adapting to the unique needs and preferences of each individual.
Annotated References:
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): Provides comprehensive information on Otosclerosis, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. NIDCD on Otosclerosis.
American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: Offers detailed insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and recent advancements in Otosclerosis. AAO-HNS on Otosclerosis.
Learn More
TINNITUS GURU
HEARING LOSS NEWS



