Otosclerosis, primarily known as an adult disorder affecting bone growth in the middle ear and causing progressive hearing loss, also presents unique challenges in pediatric cases. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis, focusing on diagnosis, management, and the psychosocial impacts of these conditions on children.
Diagnosing Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in Children
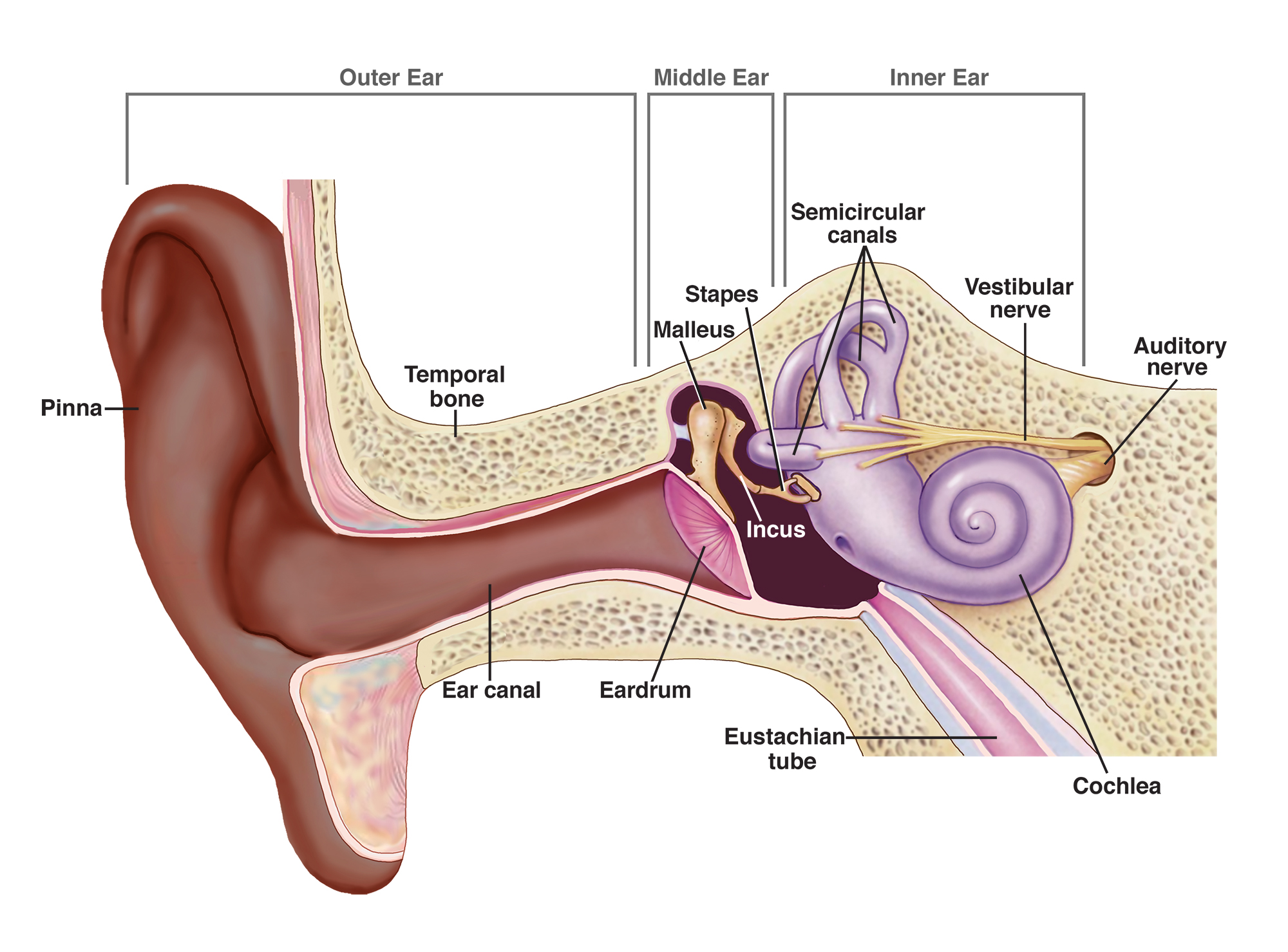
Diagnosing Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis in children is challenging due to symptom overlap with other common ear disorders and communication barriers with young patients. Medical professionals use audiometric testing, tympanometry, and CT scans for accurate diagnosis. Early detection is crucial, as it significantly improves outcomes. Managing these conditions in young people involves hearing aids, drug therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention like stapedotomy. The decision for surgery depends on the severity of hearing loss and the child’s overall health. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the management plan are essential for the child’s success.
Impact of Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis on Children’s Learning and Development
Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis can significantly impact a child’s learning and development. Hearing is crucial for language skills and communication, and these conditions can hinder academic performance and social interactions. In classrooms, affected children may struggle with instructions and group discussions, leading to frustration, alienation, and lowered self-esteem. However, with tailored learning strategies, hearing aids, speech therapy, and a nurturing environment, these effects can be mitigated, empowering the child to reach their full potential.
Supporting Teens Living with Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
Adolescence is challenging, and living with Otosclerosis or Otospongiosis adds to these challenges. Parents can improve their teen’s quality of life by fostering open communication, educating them about their condition, and providing reassurances. Addressing the psychosocial aspects is also crucial, incorporating counseling, support groups, and individual therapy. Encouraging participation in social activities fosters normalcy and positive self-esteem.
Latest Developments in Pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
Recent advancements in the understanding of pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis have led to improved diagnostic and treatment methods. These developments are crucial in managing these conditions effectively and ensuring better outcomes for affected children.
Innovative Treatments and Therapies for Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
The medical community is exploring new treatments for Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis, including medications that could halt or reverse their progression. Advances in hearing aid technology and cochlear implants have also significantly improved the quality of life for those affected.
Mental Health and Otosclerosis: Understanding the Connection
Living with Otosclerosis or Otospongiosis can have a profound impact on mental health. Studies have highlighted the increased risks of anxiety, depression, and social isolation associated with hearing loss. Addressing these mental health aspects is crucial for providing comprehensive care to individuals with these conditions.
FAQs About Pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
- What is Pediatric Otosclerosis? Pediatric Otosclerosis is a condition affecting the bones in the middle ear, leading to hearing loss in children.
- What is Otospongiosis? Otospongiosis refers to the early stages of Otosclerosis, where the bone remodeling process begins.
- How are Pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis diagnosed? They are diagnosed through hearing tests, tympanometry, and CT scans.
- Can these conditions lead to complete hearing loss in children? In severe cases, they can lead to complete hearing loss, but early detection and treatment can slow or halt this progression.
- Are there new treatments for these conditions? Yes, recent research is exploring innovative treatments and therapies for Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis.
- Do these conditions affect children’s mental health? Yes, they can lead to increased risks of anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Practical Tips for Managing Pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis
- Regular Hearing Assessments: Regular visits to an audiologist are essential for monitoring hearing loss in children.
- Utilize Assistive Technologies: Hearing aids and other devices can greatly improve hearing capabilities in children.
- Stay Informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest research and treatment options is beneficial for parents and caregivers.
- Join Support Networks: Connecting with others who have children with these conditions can provide valuable support and information.
- Encourage Open Communication: Helping children express their feelings and concerns about their condition is crucial for their mental well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding pediatric Otosclerosis and Otospongiosis goes beyond the scope of hearing loss. Comprehending the potential connections between these conditions and their impact on children’s learning, development, and mental health can provide a more comprehensive view of the condition. This understanding allows for a more holistic approach to care, focusing not only on the ear but also on the overall well-being of the child.
Annotated References:
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): Provides comprehensive information on Otosclerosis, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. NIDCD on Otosclerosis.
American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: Offers detailed insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and recent advancements in Otosclerosis. AAO-HNS on Otosclerosis.
Learn More
TINNITUS GURU
HEARING LOSS NEWS



